-
In the intricate models designed to elucidate the chemical evolution of s-isotopes, considerable attention has been directed toward the pivotal roles played by abundant light nuclei, namely,
$ ^{12}\mathrm C $ ,$ ^{16}\mathrm O $ , and$^{20} \mathrm {Ne}$ . These nuclei have been posited as potential neutron poisons [1], where their substantial neutron capture cross sections could significantly impact the production of heavier s-isotopes. Correspondingly, the yields of p-process nuclei may also experience a decrease, given that s-process nuclei are perceived as immediate precursors to p-nuclei [2]. In recent years, there has been a notable increase in research interest centered on the nuclear reactions$ ^{12}\mathrm C(n,\gamma)^{13}\mathrm C $ and$ ^{16}\mathrm O(n,\gamma)^{17}\mathrm O $ [3] aimed at understanding various astrophysical processes and cosmic nucleosynthesis. It is worth noting that inhomogeneous Big-Bang models [4] have predicted a substantial production of intermediate heavy nuclei within neutron-rich regions through a sequential process involving reactions such as$^{12}\mathrm C(n,\gamma) ^{13}\mathrm C(n,\gamma) ^{14}\mathrm C(p, \gamma)^{15}\mathrm N(n, \gamma)^{16}\mathrm N(\beta^{-})^{16}\mathrm O(n,\gamma)^{17}\mathrm O$ . Consequently, to construct accurate predictive models for the production of s- and p-isotopes and to quantitatively estimate the yields of heavy elements within the framework of inhomogeneous Big-Bang models, acquiring precise knowledge of neutron capture cross sections for these light nuclei at stellar neutron energies assumes paramount importance.Indeed, it is important to highlight that inhomogeneous Big Bang models put forth the notion that there is a substantial generation of intermediate heavy nuclei in regions that are abundant in neutrons. This generation occurs through a sequential process that involves a series of nuclear reactions. Consequently, to construct precise and reliable models for forecasting the production of s-isotopes (isotopes with an excess of neutrons) and p-isotopes (proton-rich isotopes), and to quantitatively estimate the production rates of heavy elements within these inhomogeneous Big Bang scenarios, it becomes imperative to acquire an accurate understanding of the neutron capture cross sections of light nuclei. Ohsaki et al. [5] conducted experiments to measure the cross-section of the
$ ^{12}\mathrm C(n,\gamma)^{13}\mathrm C $ reaction within a neutron energy range of 10 to 250 keV. In contrast, Macklin [6] performed similar experiments but focused on a different energy spectrum, ranging from 0.1 keV to 2 MeV. Previous efforts have aimed to investigate nuclear structure details through the utilization of (n, γ) reactions with astrophysical relevance. In the direct radiative capture (DRC) process involving p-wave neutrons [7], a sensitivity assessment of the neutron-nucleus potential has been carried out for energies in the keV range. It has been observed that, in the same process, s-wave neutrons are significantly affected by the neutron-nucleus potential, whereas p-wave neutrons exhibit insensitivity to a similar type of interaction, particularly at very low energies where p-wave neutron collisions remain peripheral and unaffected by the neutron-nucleus potential [8]. In their work, Kikuchi et al. [8] adopted spectroscopic values for negative parity states, the ground and second excited states of$^{13}{\rm C}$ , from the (d, p) reaction [9]. A notable discrepancy has been noted in the measurement of the capture cross section for the third excited state of$^{13}{\rm C}$ at${5}/{2}^+$ , which introduces significant uncertainty in the spectroscopic factor for this transition. Furthermore, the presence of resonance in close proximity to the threshold leads to interference between the resonant and DRC processes. However, the weak resonance at 46 keV suggested by Macklin 1990 [6] was not confirmed by the experimental findings of Ohsaki et al. [5]. To resolve this type of discrepancies, we employed the R-matrix code AZURE2 [10, 11] using experimental data obtained by Ohsaki et al. [5] to compute the reaction cross-section at energy levels with significance in astrophysical contexts. This approach allows us to extend our understanding of this reaction's behavior under conditions relevant to astrophysical processes. If you require further assistance with data analysis or calculations pertaining to the phenomenological R-matrix of this research, please refer to our recent paper involving the R-matrix approach [3]. -
The γ-ray emissions originating from the captured state of
$ ^{13}\mathrm C $ at various energy levels are observable. These emissions include transitions to the ground state ($ J^{\pi}=1/2^{-} $ ) at 0.0 keV, the first excited state ($ J^{\pi}=1/2^{+} $ ) at 3089 keV, the second excited state ($ J^{\pi}=3/2^{-} $ ) at 3684 keV, and the third excited state ($ J^{\pi}=5/2^{+} $ ) at 3854 keV. Additionally, gamma-ray emissions from these excited states back to the ground state are also evident [12]. Particularly prominent is the transition to the$ J^{\pi}=1/2^{+} $ first excited state by 30 keV neutrons. This outcome stands in contrast to γ-ray transitions originating from the captured state of$ ^{13}\mathrm C $ induced by thermal neutrons (Lone 1982). Strong$E1 \;\;\gamma$ -transitions to the$ J^{\pi}=1/2^{-} $ ground state and the$ J^{\pi}=3/2^{-} $ second excited state were observed.In the present case, we observed that the partial capture cross sections exhibit different behaviors when transitioning from a captured state to various nuclear states. Specifically, the cross sections for transitions to the ground state (
$ 1/2^{-} $ ) and the second excited state ($ 3/2^{-} $ ) closely agree with values extrapolated based on the$ 1/v $ law. However, the partial capture cross section for the transition to the first excited state ($ 1/2^{+} $ ) does not conform to this extrapolated value. Instead, it shows an increasing trend with the laboratory neutron energy,$E_{\rm lab}$ , and the neutron energy in the c.m frame,$E_{\rm c.m} = E_{\rm lab} \times \frac{12}{13}$ . This energy-dependent behavior of the partial capture cross section suggests that, as the neutron energy increases, the dominant capture mechanism involves p-wave interactions. This conclusion is drawn from the assumption that the primary decay mode from a captured state to a nearby state is E1 (electric dipole) [5]. The s-wave capture dominates at$ E_n \leq 100 $ keV, whereas the d-wave component becomes crucial at higher energies [8]. -
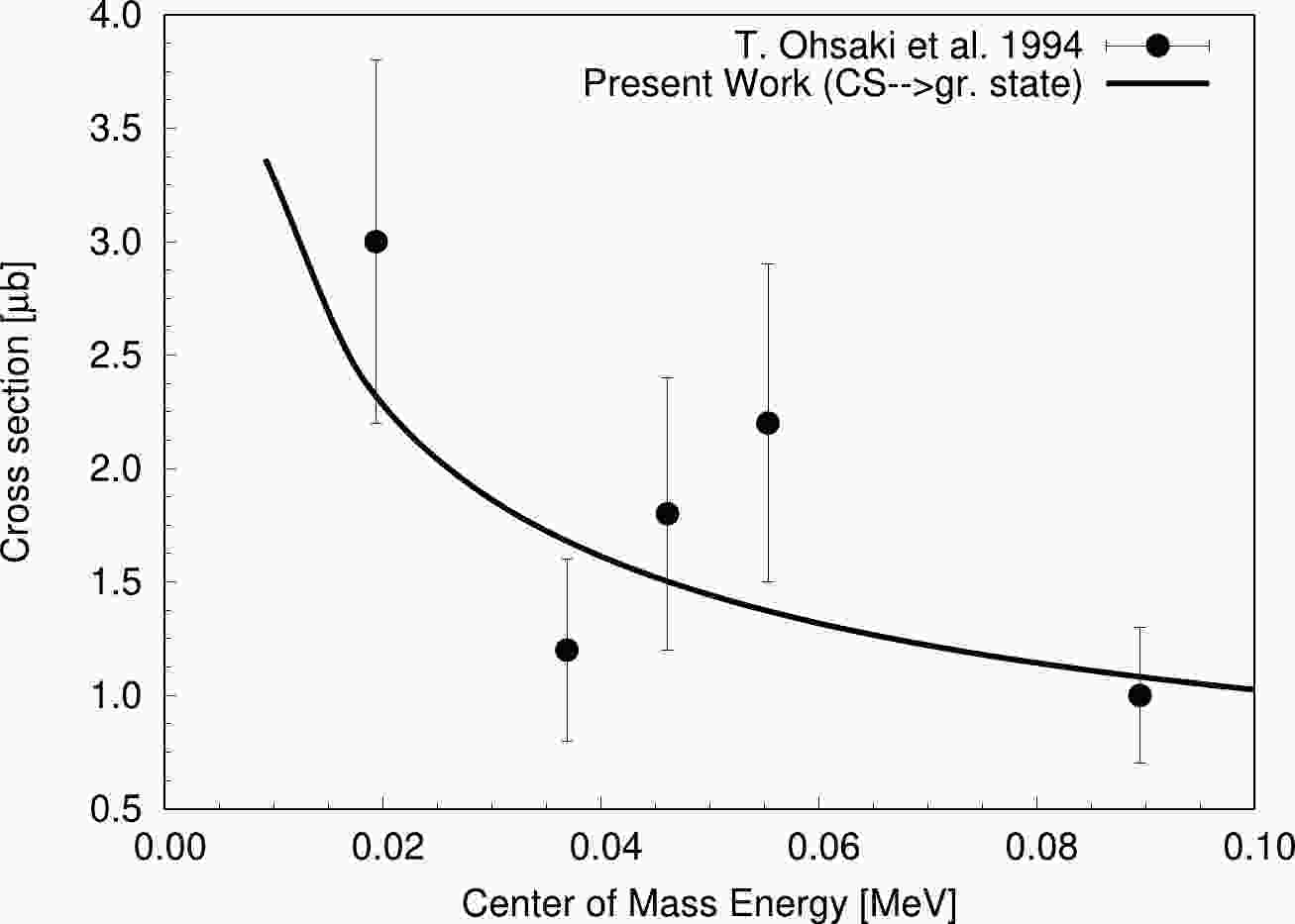
In the present study, cross sections for the ground, first, second, and third excited state transitions with neutron energies following the R-matrix analysis were determined and are shown in Fig. 1, Fig. 2, Fig. 3, and Fig. 4, respectively, and the total capture cross section obtained in the R-matrix analysis is shown in Fig. 5. The optimal R-matrix parameters are presented in Table 1. We obtained the reaction rates of the
$ ^{12}\mathrm C(n,\gamma)^{13}\mathrm C $ reaction (in the range of$ 10^7 - 10^9 $ ), which are listed in Table 2. The total$ \chi ^2 $ value is 1.13. At$ kT = 30 $ keV, the cross section is estimated to be less than or equal to 11.98$ \pm $ 0.25 μb, whereas a lower limit of 3.2 μb is derived from extrapolating the measured thermal cross section based on the$ 1/v $ law [6]. Our discoveries hold significance for the nucleosynthesis outcomes in non-uniform primordial nucleosynthesis models.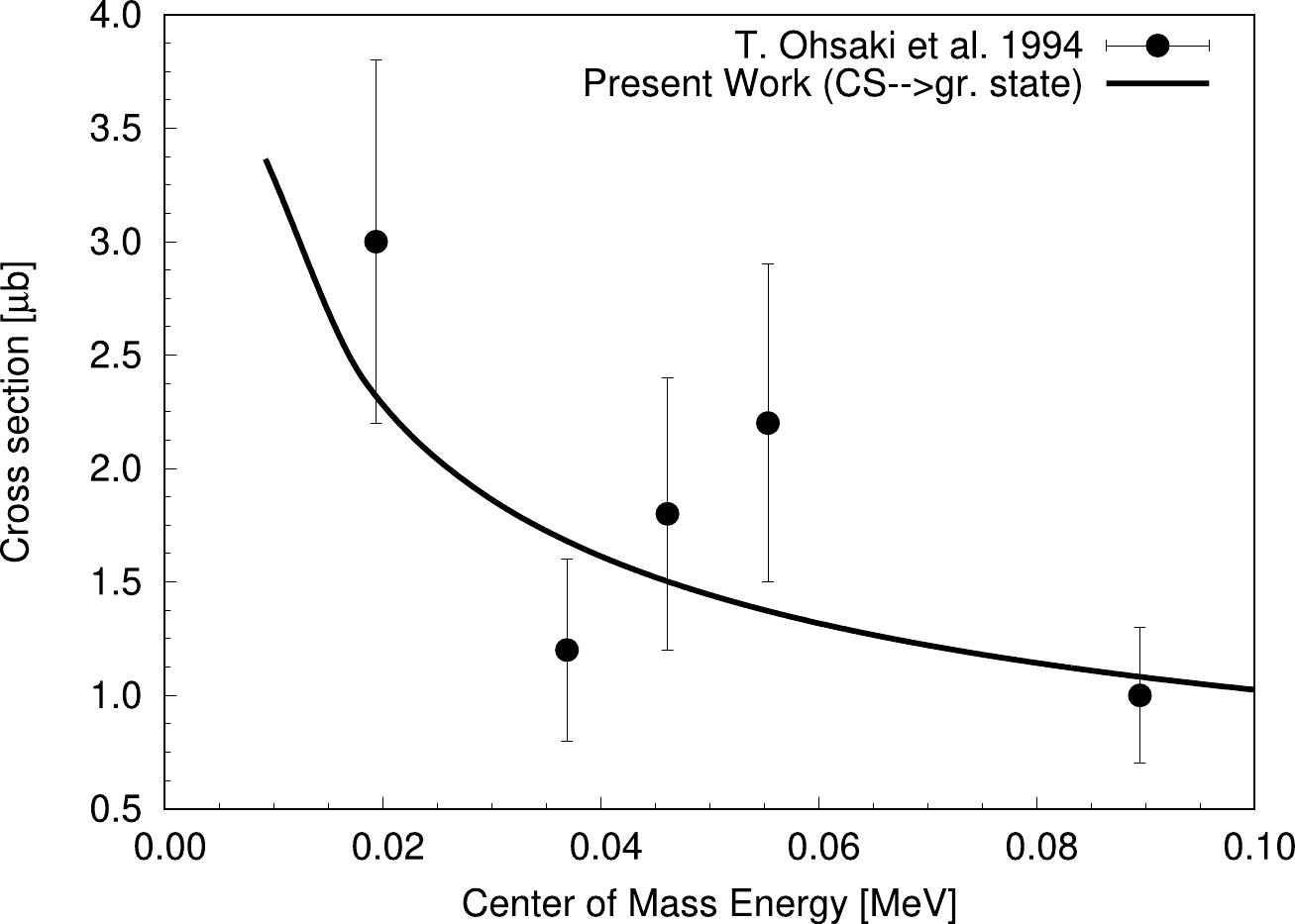
Figure 1. Variation of the
$ ^{13}\mathrm C $ captured state to ground state reaction cross section with CM energy for$ ^{12}\mathrm C(n,\gamma)^{13}\mathrm C $ using best-fit R-matrix analysis. Plotted data with errorbars are extracted from Ohsaki et al. (1994) [5].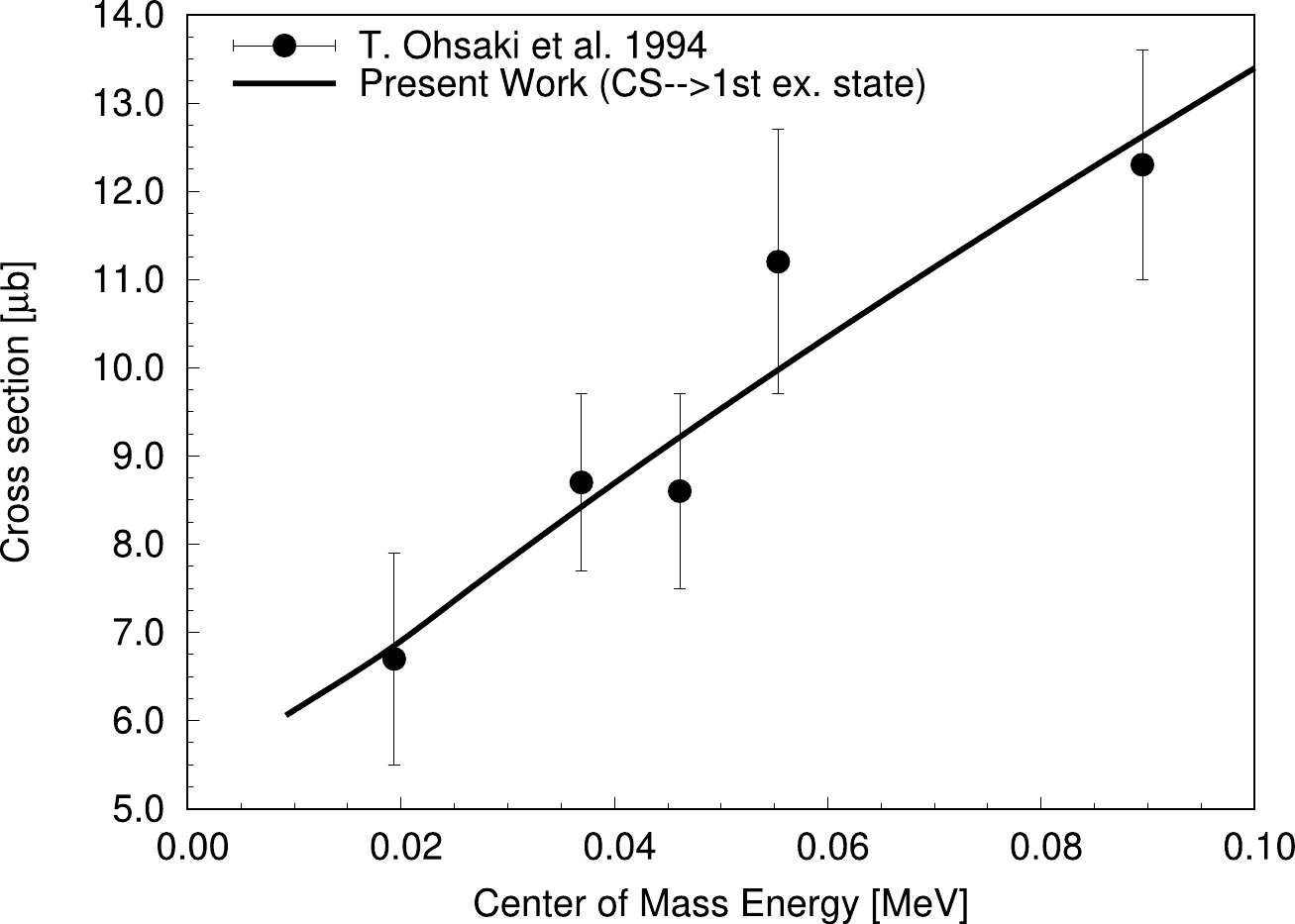
Figure 2. Variation of the
$ ^{13}\mathrm C $ captured state to first excited state reaction cross section with CM energy for$ ^{12}\mathrm C(n,\gamma)^{13}\mathrm C $ using best-fit R-matrix analysis. Plotted data with errorbars are extracted from Ohsaki et al. (1994) [5].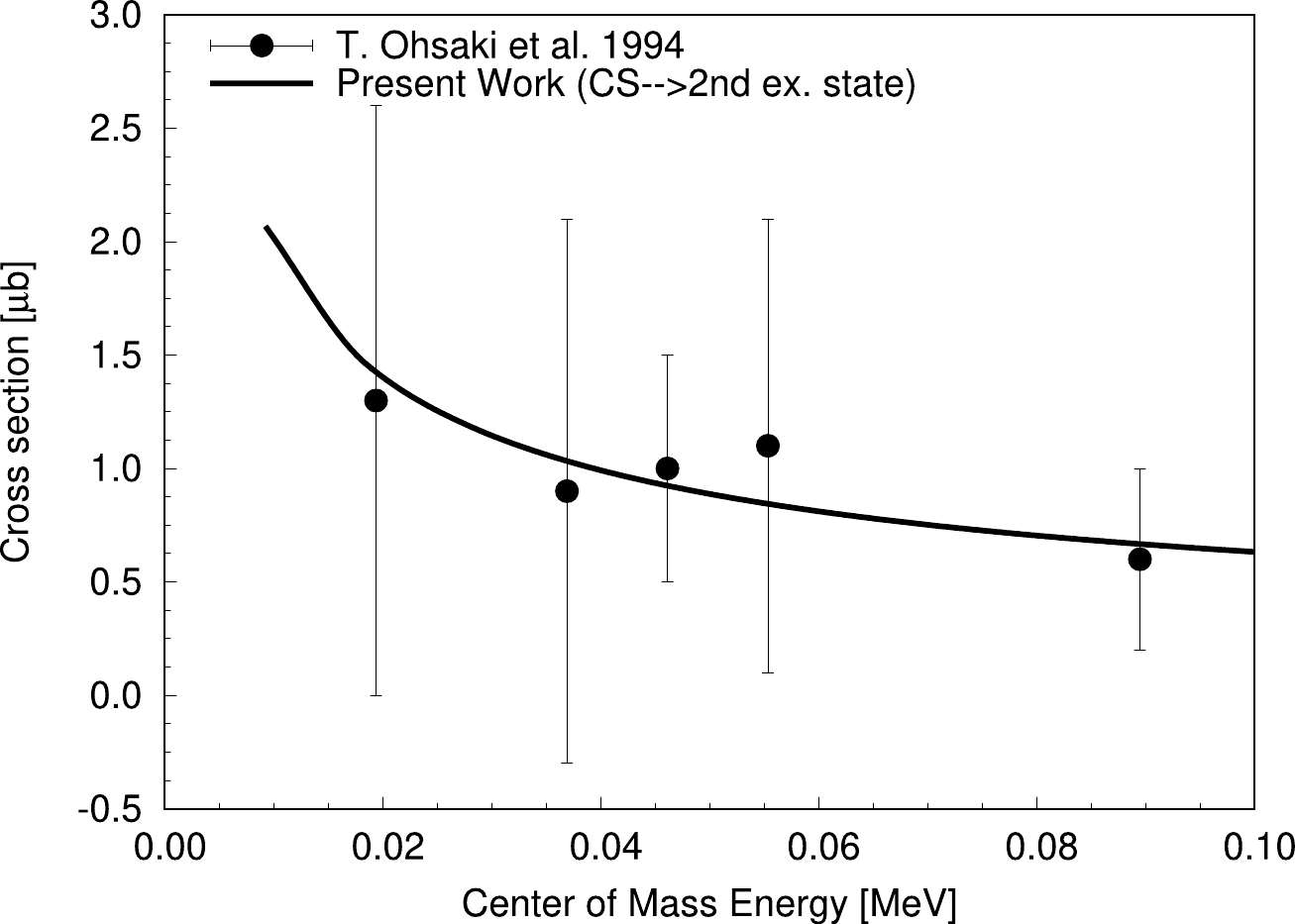
Figure 3. Variation of the
$ ^{13}\mathrm C $ captured state to second excited state reaction cross section with CM energy for$ ^{12}\mathrm C(n,\gamma)^{13}\mathrm C $ using best-fit R-matrix analysis. Plotted data with errorbars are extracted from Ohsaki et al. (1994) [5].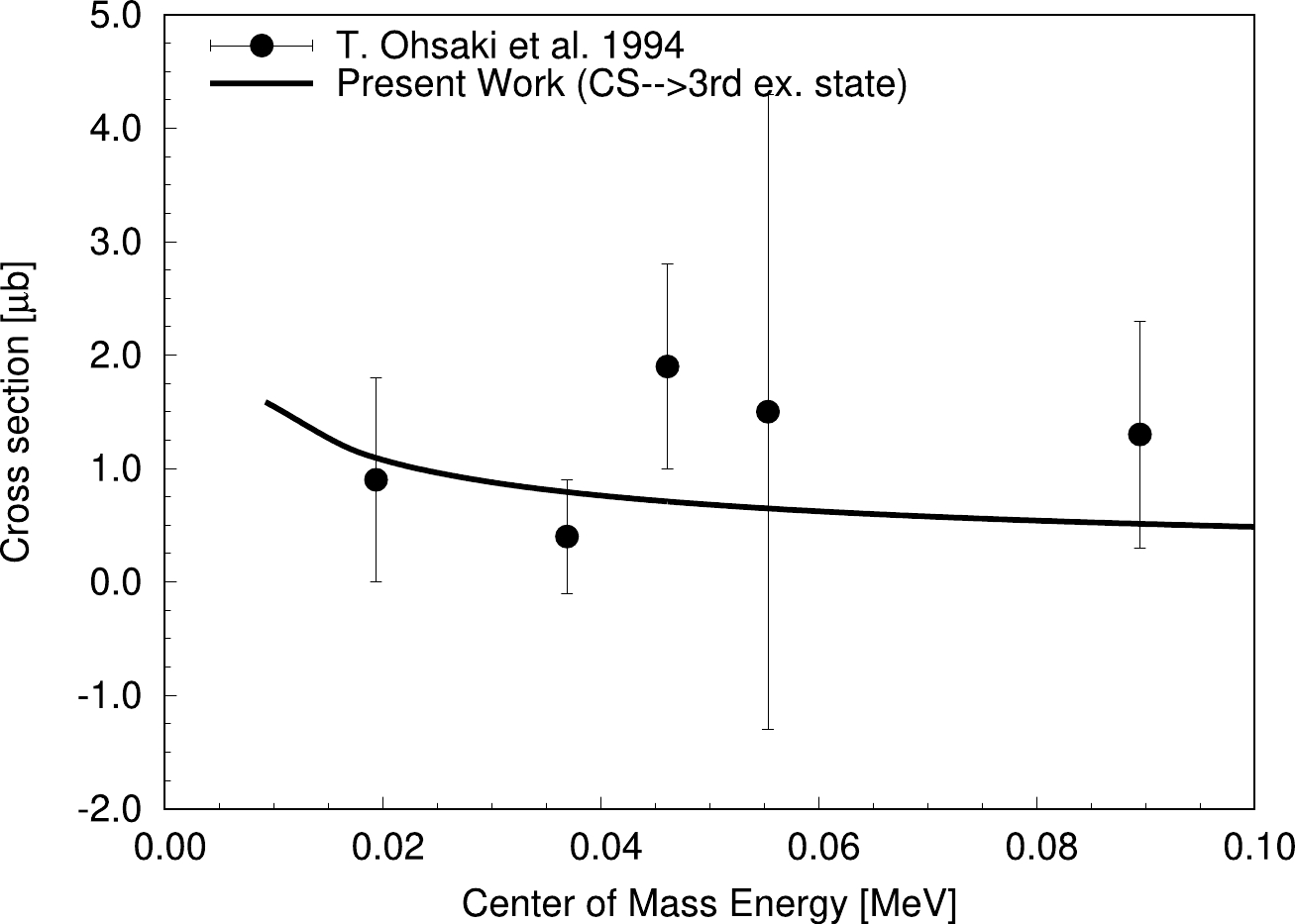
Figure 4. Variation of the
$ ^{13}\mathrm C $ captured state to third excited state reaction cross section with CM energy for$ ^{12}\mathrm C(n,\gamma)^{13}\mathrm C $ using best-fit R-matrix analysis. Plotted data with errorbars are extracted from Ohsaki et al. (1994) [5].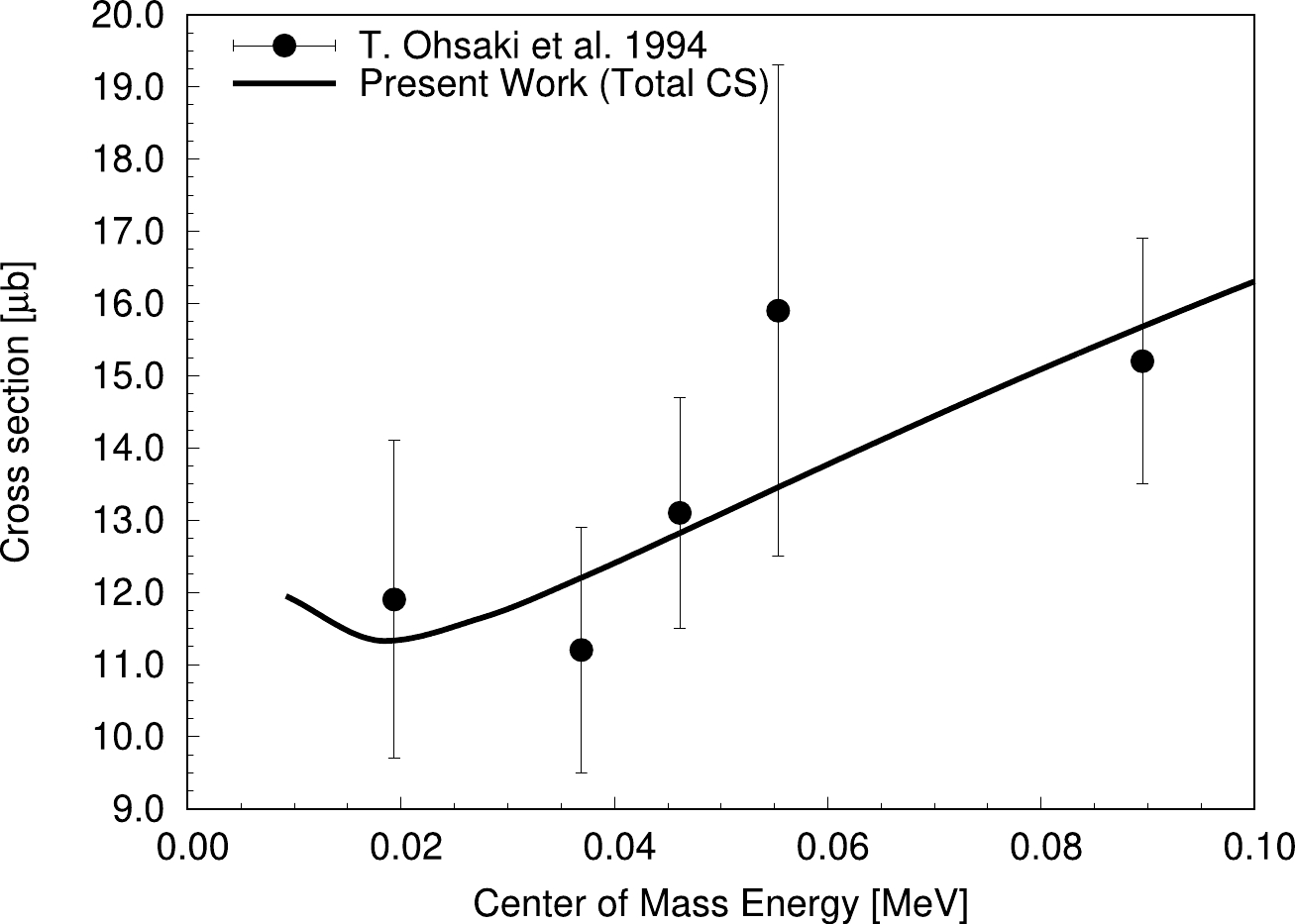
Figure 5. Variation of the total reaction cross section with CM energy for
$ ^{12}\mathrm C(n,\gamma)^{13}\mathrm C $ using best-fit R-matrix analysis. Plotted data with errorbars are extracted from Ohsaki et al. (1994) [5].Level
SpinEnergy
/MeVChannel
Pairl/Multi-
polarityFitted
parameters$ 1/2- $ 

0.0 $^{12}{\rm C}+n$ 

$ 1 $ 

ANC=6.03 fm−1/2 $ 1/2+ $ 

3.089 $^{12}{\rm C}+n$ 

0 ANC=2.85 fm−1/2 $ 3/2- $ 

3.684 $^{12}{\rm C}+n$ 

1 ANC=0.23 fm−1/2 $ 5/2+ $ 

3.853 $^{12}{\rm C}+n$ 

1 ANC=0.11 fm−1/2 $ 5/2+ $ 

6.864 $^{13}{\rm C}+\gamma$ 

M2 Γ =6.02 keV $ 5/2- $ 

7.547 $^{13}{\rm C}+\gamma$ 

E2 Γ=1.21 keV $ 3/2+ $ 

7.686 $^{13}{\rm C}+\gamma$ 

E1 Γ=69.9 keV Table 1. Fitted R-matrix parameters in the compound nucleus
$ ^{13} $ C and the allowed decay channels (allowed maximum orbital momentum of 3, maximum gamma multipolarity of 2, and maximum of 2 gamma multiplicities per decay).Temperature in GK Reaction Rates in cm3 mol−1 s−1 0.01 375 0.06 905 0.11 1167 0.16 1417 0.21 1665 0.26 1913 0.31 2160 0.36 2407 0.41 2652 0.46 2897 0.51 3139 0.56 3380 0.61 3620 0.66 3858 0.71 4094 0.76 4328 0.81 4561 0.86 4792 0.91 5021 0.96 5249 1.01 5475 Table 2. Nuclear reaction rates of
$ ^{12}\mathrm C(n,\gamma)^{13}\mathrm C $ obtained in R-matrix analysis. -
In our theoretical investigation, we conducted measurements of the reaction cross sections associated with the
$ ^{12}\mathrm C(n,\gamma)^{13}\mathrm C $ reaction within the nuclear astrophysical energy range of significance. These findings bear significant ramifications for the s-process nucleosynthesis in low-metallicity asymptotic giant branch (AGB) stars. Specifically, in the reaction cross sections of$ ^{12}\mathrm C $ , a moderately less effective neutron-absorbing agent or neutron poison was found in these environments, which is in contrast to the findings in the study of Ohsaki et al. [5]. This result is substantiated by our calculations of nuclear reaction rates of astrophysical importance.This refined comprehension of the underlying mechanisms forms the fundamental basis for enhancing our knowledge of the nucleosynthesis procedures that have played a pivotal role in shaping the elemental composition of the cosmos. Ultimately, our work contributes to unraveling the intricate details of cosmic evolution and knowledge thereof.
-
We express our gratitude to G. Gangopadhyay for his valuable support in managing this work.
Cosmic implications of the ${^{12}{\bf C}(\boldsymbol n,\bf\gamma)^{13}{\bf C} }$ reaction: a nuclear astrophysical perspective
- Received Date: 2023-10-08
- Available Online: 2024-02-15
Abstract: We conducted a comprehensive study of the neutron capture cross section of






 Abstract
Abstract HTML
HTML Reference
Reference Related
Related PDF
PDF
















 DownLoad:
DownLoad: