Highlights
-
Pear shape and tetrahedral shape competition in actinide nuclei
2025, 49(7): 074110. doi: 10.1088/1674-1137/add5d0
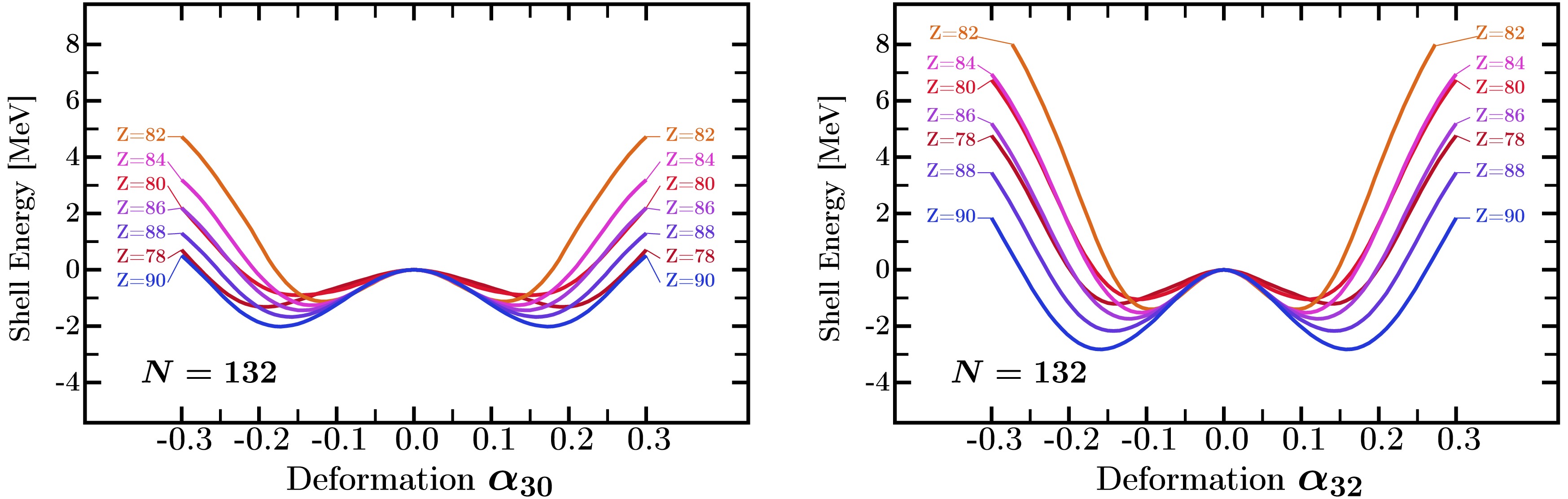 Shape competition and coexistence between the pear- and the tetrahedral-shape octupole deformations in actinide nuclei is investigated by employing the realistic nuclear mean-field theory with the phenomenological, so-called 'universal' Woods-Saxon Hamiltonian with newly adjusted parameters containing no parametric correlations. Both types of octupole deformations exhibit significant effects in
Shape competition and coexistence between the pear- and the tetrahedral-shape octupole deformations in actinide nuclei is investigated by employing the realistic nuclear mean-field theory with the phenomenological, so-called 'universal' Woods-Saxon Hamiltonian with newly adjusted parameters containing no parametric correlations. Both types of octupole deformations exhibit significant effects in$ N=132 $ ,$ N=134 $ , and$ N=136 $ isotones. Nuclear potential energy calculations within the multi-dimensional deformation spaces reveal that the tetrahedral deformation effects generally lead to deeper energy minima in most nuclei with$ N=134 $ and$ N=136 $ . Interestingly, in the nuclei$^{218}_{\;\;86}{\rm{Rn}}_{132} $ ,$^{222}_{\;\;88}{\rm{Ra}}_{134} $ , and$^{222}_{\;\;86}{\rm{Rn}}_{136} $ , selected for the illustration of the studied effects, the influence of pear-shape octupole deformation is comparable to that of tetrahedral octupole deformation. Consequently, the coexistence of both kinds of octupole shapes is predicted by the potential energy calculations. In particular, we have reproduced the experimental results known for pear-shape rotational bands obtaining in this way an estimate of the quality of the modelling parametrisation. With the same Hamiltonian, we have predicted the properties of the tetrahedral symmetry rotational bands. To facilitate the possible experiment-theory cooperation we have derived the exact spin-parity tetrahedral-band structures by applying the standard methods of the group representation theory for the Td point-group. -
Cluster radioactivity half-lives within deformed Gamow-like model
2025, 49(7): 074105. doi: 10.1088/1674-1137/adc097
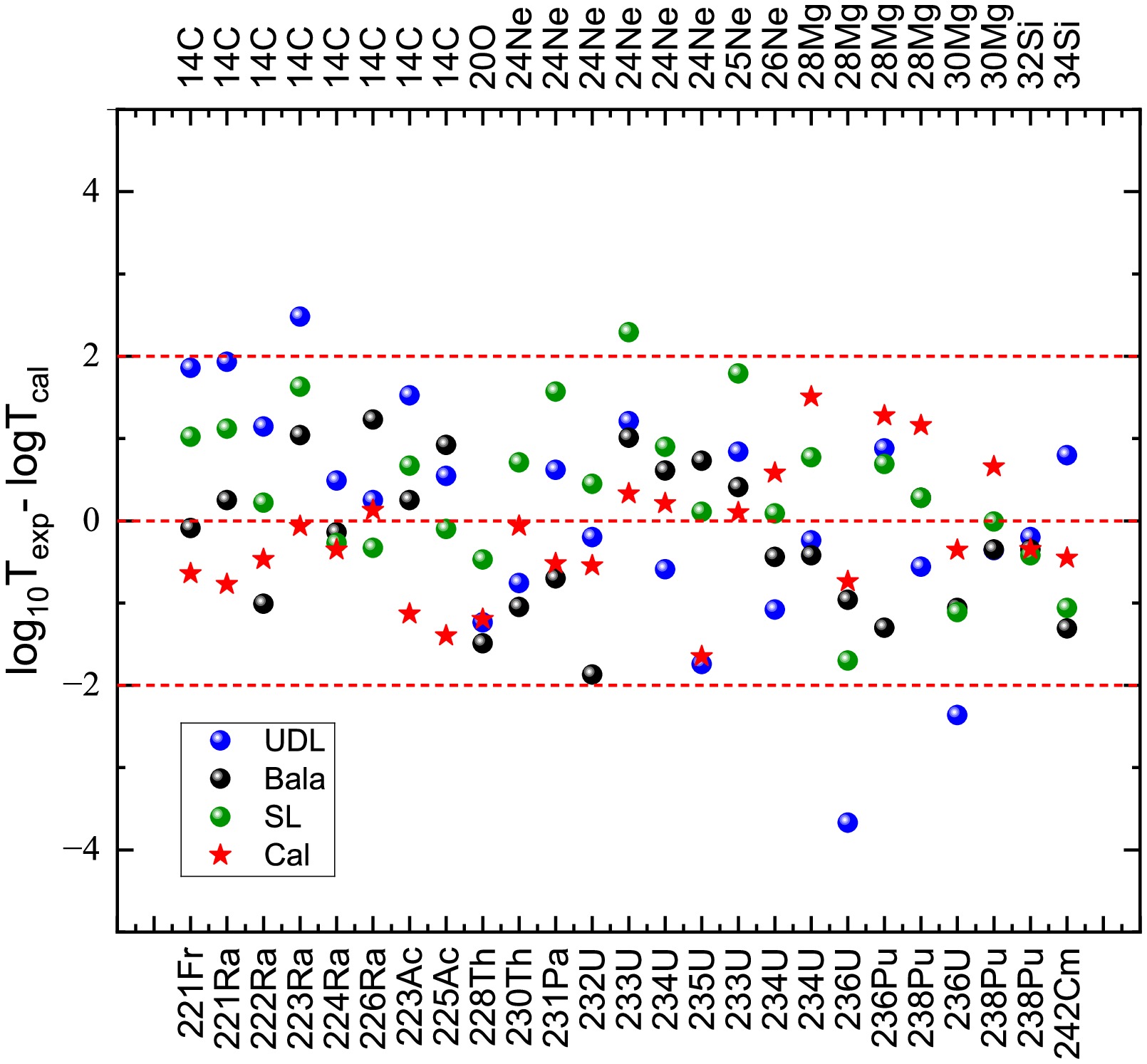 In the present work, based on a Gamow-like model, considering the deformation effect of Coulomb potential, where the effective nuclear radius constant is parameterized, we systematically investigate the cluster radioactivity half-lives of 25 trans-lead nuclei. For comparison, a universal decay law (UDL) proposed by Qi et al. [Phys. Rev. C 80, 044326 (2009)], a new semi-empirical formula for exotic cluster decay proposed by Balasubramaniam et al. [Phys. Rev. C 70, 017301 (2004)], and a scaling law proposed by Horoi [J. Phys. G: Nucl. Part. Phys. 30, 945 (2004)] are also used. The calculated results within the deformed Gamow-like model are in better agreement with the experimental half-lives. The deformation effect is also discussed within both the Gamow-like and deforemed Gamow-like models. Moreover, we extend this model to predict the cluster radioactivity half-lives of 49 nuclei whose decay energies are energetically allowed or observed but not yet quantified in NUBASE2020.
In the present work, based on a Gamow-like model, considering the deformation effect of Coulomb potential, where the effective nuclear radius constant is parameterized, we systematically investigate the cluster radioactivity half-lives of 25 trans-lead nuclei. For comparison, a universal decay law (UDL) proposed by Qi et al. [Phys. Rev. C 80, 044326 (2009)], a new semi-empirical formula for exotic cluster decay proposed by Balasubramaniam et al. [Phys. Rev. C 70, 017301 (2004)], and a scaling law proposed by Horoi [J. Phys. G: Nucl. Part. Phys. 30, 945 (2004)] are also used. The calculated results within the deformed Gamow-like model are in better agreement with the experimental half-lives. The deformation effect is also discussed within both the Gamow-like and deforemed Gamow-like models. Moreover, we extend this model to predict the cluster radioactivity half-lives of 49 nuclei whose decay energies are energetically allowed or observed but not yet quantified in NUBASE2020. -
Transfer reaction products in the 40Ar + 232Th reaction
2025, 49(7): 074004. doi: 10.1088/1674-1137/adcb96
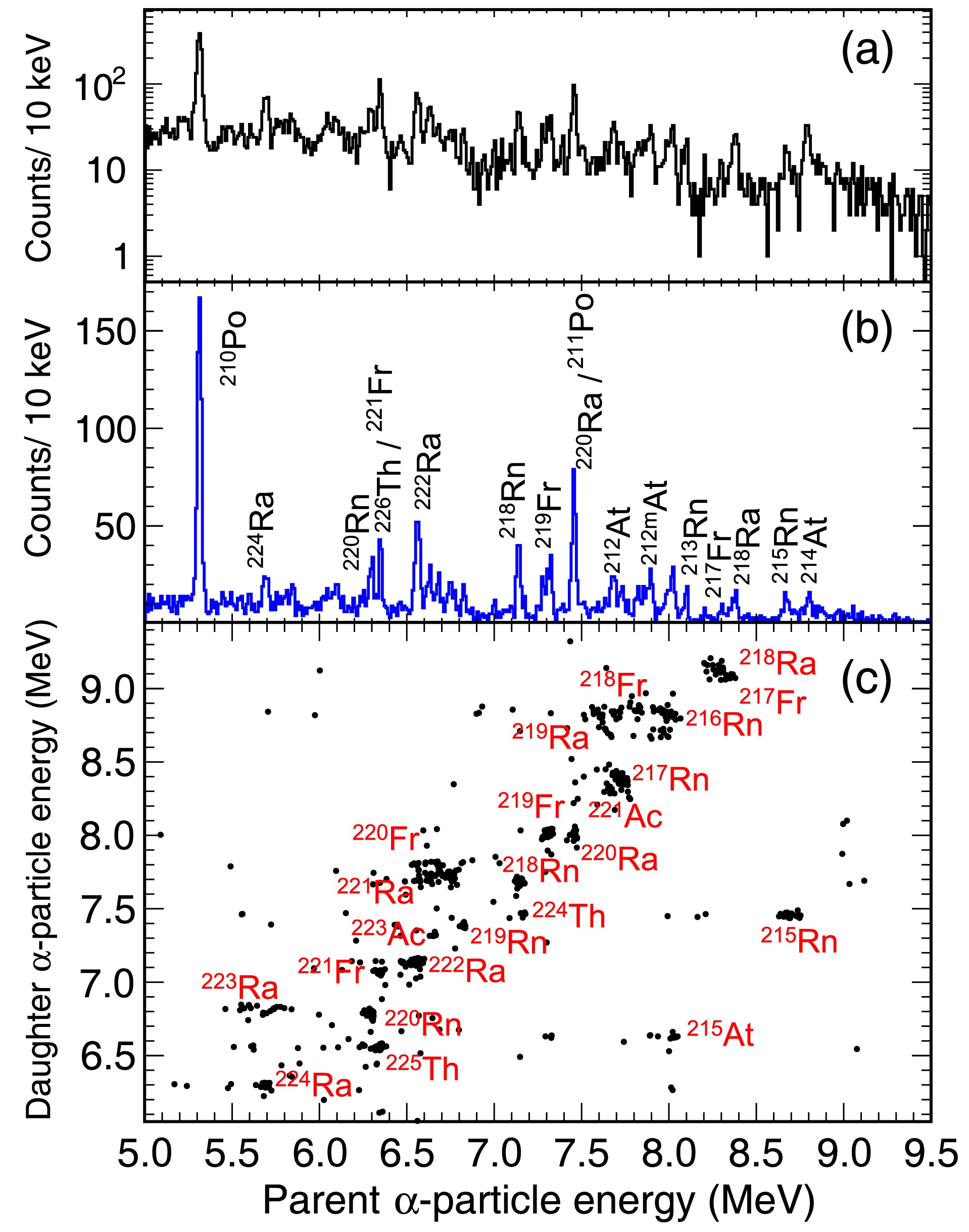 The distribution of nuclei produced in the 40Ar + 232Th reaction has been studied at the gas-filled recoil separator (SHANS2) at the China Accelerator Facility for Superheavy Elements (CAFE2). The bombardment was carried out at a beam energy of 205 MeV with the detection system installed at the focal plane. Forty-four isotopes heavier than 208Pb were observed. These isotopes were identified as the transfer reaction (or target-like) products, and their relative cross-sections were extracted. Based on the mass distribution of these products, we exclude the possibility that they were produced by fusion-fission reactions; thus, they may originate from quasi-fission of the 40Ar + 232Th reaction.
The distribution of nuclei produced in the 40Ar + 232Th reaction has been studied at the gas-filled recoil separator (SHANS2) at the China Accelerator Facility for Superheavy Elements (CAFE2). The bombardment was carried out at a beam energy of 205 MeV with the detection system installed at the focal plane. Forty-four isotopes heavier than 208Pb were observed. These isotopes were identified as the transfer reaction (or target-like) products, and their relative cross-sections were extracted. Based on the mass distribution of these products, we exclude the possibility that they were produced by fusion-fission reactions; thus, they may originate from quasi-fission of the 40Ar + 232Th reaction.
Just Accepted
More >
-
Gravitationally deformed polytropic models in extended teleparallel gravity and influence of decoupling parameters on constraining mass-radius relation
Published: 2025-06-26
-
The role and contribution of resonance effect for the decay process of
${ \bar {\boldsymbol B}^{\bf 0}_{\boldsymbol s} \boldsymbol\rightarrow \boldsymbol\pi^{+}\boldsymbol\pi^{-}{\boldsymbol P}}$ Published: 2025-06-26 -
An Unitary Coupled-Channel Approach to J/ψ Radiative decay to Pseudoscalar Pairs
Published: 2025-06-24
Recent
More >
-
Schottky detection techniques for ultra-rare short-lived ions in heavy-ion storage rings
2025, 49(8): 1-5. doi: 10.1088/1674-1137/adcc00Show AbstractNon-destructive Schottky detectors are indispensable devices widely used in experiments at heavy-ion storage rings. In particular, they can be used to accurately determine the masses and lifetimes of short-lived exotic nuclear species. Single-ion sensitivity – which is the highest level of sensitivity – has been regularly achieved in the past by utilizing resonant cavity detectors. Recent designs and analysis methods aim to push the limits of measurement accuracy by increasing the dimensionality of the acquired data, namely, the position of the particle as well as the phase difference between several detectors. This paper describes current methods and future perspectives for Schottky detection techniques, with a focus on their application to mass and lifetime measurements of the most rare and simultaneously short-lived radio nuclides.
-
Invariant mass spectroscopy of 15C
2025, 49(8): 084001-084001-8. doi: 10.1088/1674-1137/add10cShow AbstractInvariant-mass spectroscopy has been performed to search for possible resonance states in the loosely bound neutron-rich 15C nucleus. By detecting alpha and 11Be in coincidence, we reconstruct the excitation energy spectrum for 15C. To estimate the physical background from non-resonant prompt alpha particles, we employ a recently proposed weighted event-mixing method with phenomenological reduced weighting at around the alpha-decay threshold to account for the depletion in the prompt alpha's contribution owing likely to the Coulomb final-state interactions. A new weighted mixed-event method that focuses on a robust treatment of the Coulomb effect is also proposed. Through fitting the spectrum using the background estimated with these two methods, up to two resonance state candidates are proposed. Further experiments with improved statistics and theoretical calculations are called for to confirm these resonance states.
-
A novel jet model for the Novikov-Thorne disk and its observable impact
2025, 49(8): 1-7. doi: 10.1088/1674-1137/add10eShow AbstractRecent high-resolution observations have established a strong link between black hole jets and accretion disk structures, particularly in the 3.5 mm wavelength band [Nature. 616,686 (2023)]. In this work, we propose a "jet-modified Novikov-Thorne disk model" that explicitly incorporates jet luminosity into the accretion disk radiation framework. By integrating synchrotron radiation from relativistic electrons in the jet, we derive a modified luminosity function that accounts for both the accretion disk and jet contributions. Our analysis demonstrates that the inclusion of jet luminosity enhances the total accretion disk luminosity by approximately 33.5%, as derived from the integration of radiative flux. Furthermore, we compare our modified model with the standard Novikov-Thorne model and find that the jet contribution remains significant across different observational inclinations. These results highlight the necessity of incorporating jet effects when estimating the observable flux of black hole accretion systems, which has direct implications for future astronomical observations.
Archive
ISSN 1674-1137 CN 11-5641/O4
Original research articles, Ietters and reviews Covering theory and experiments in the fieids of
- Particle physics
- Nuclear physics
- Particle and nuclear astrophysics
- Cosmology
Author benefits
- A SCOAP3 participating journal - free Open Access publication for qualifying articles
- Average 24 days to first decision
- Fast-track publication for selected articles
- Subscriptions at over 3000 institutions worldwide
- Free English editing on all accepted articles
News
- Chinese Physics C Outstanding Reviewer Award 2023
- Impact factor of Chinese Physics C is 3.6 in 2022
- 2022 CPC Outstanding Reviewer Awards
- The 2023 Chinese New Year-Office closure
- 《Chinese Physics C》BEST PAPER AWARDS 2022
Cover Story
- Cover Story (Issue 1, 2025) Comments on Prediction of Energy Resolution inthe JUNO Experiment
- Cover Story (Issue 12, 2024) | Doubly heavy meson puzzle: precise prediction of the mass spectra and hadronic decay with coupled channel effects to hunt for beauty-charm family
- Cover Story (Issue 9, 2024) Measurement of solar pp neutrino flux using electron recoil data from PandaX-4T commissioning run
- Cover Story (Issue 11, 2024) | Form factor for Dalitz decays from J/ψ to light pseudoscalars
- Cover Story (Issue 3, 2024) | First measurement of the ground-state mass of 22Al helps to evaluate the ab-initio theory